The Bourbon King, The Inside Story: Imogene, Femme Fatale or Pawn in Remus’s Evil World?
Imogene Remus sits for a formal portrait in her finest fur shawl and feathered hat. Her stunning diamond wedding ring is prominently displayed, which may indicate that this photo was taken shortly after she and George were married in Newport, Kentucky, on June 25, 1920.
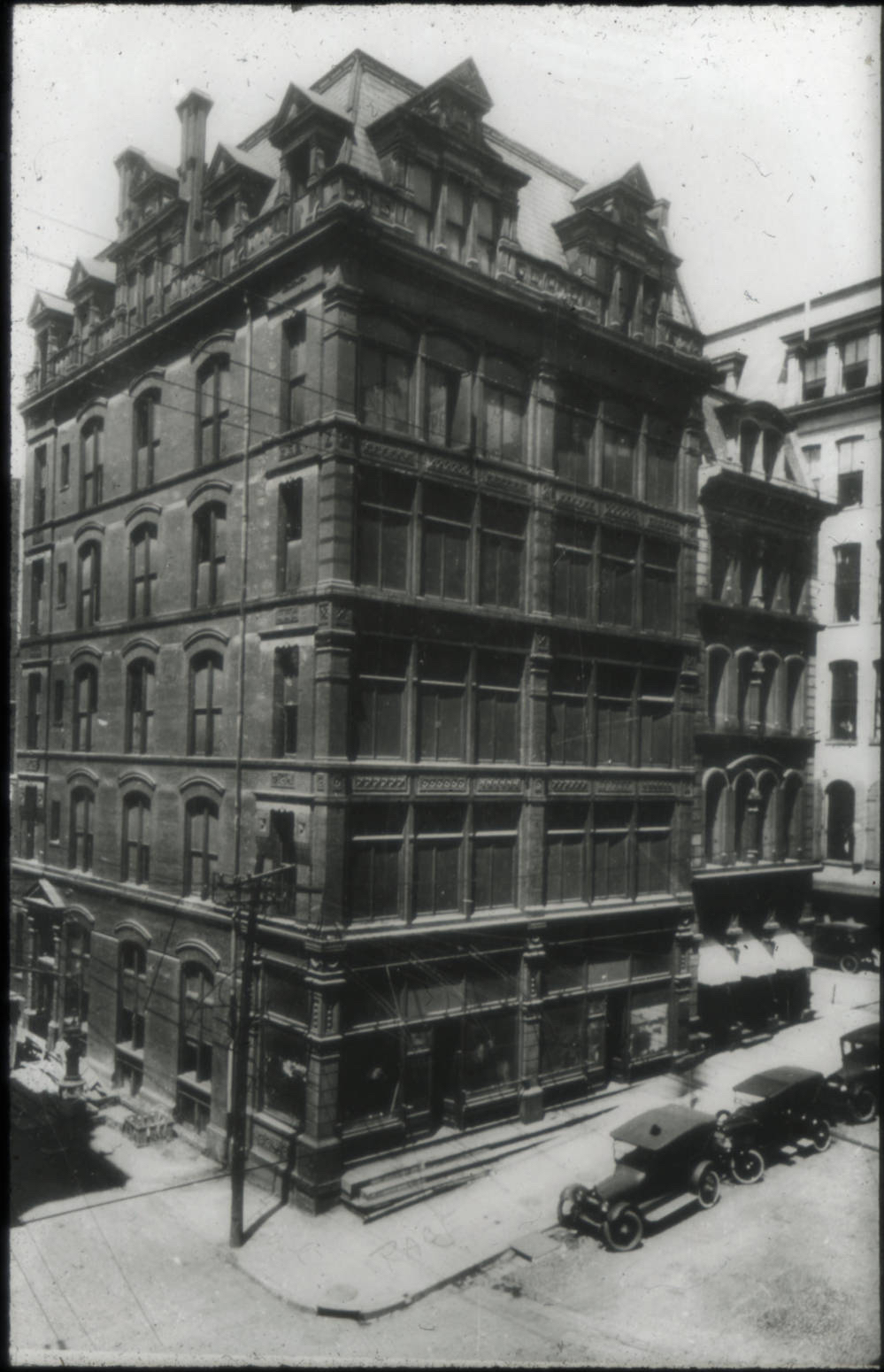
The exterior of the Gatsby-like “Dream Palace.”
Imogene Remus — Femme Fatale or Pawn in Remus’s Evil World?
Imogene Remus is one of the trickiest characters in The Bourbon King.
Imogene’s motivations and subsequent actions enabled her to easily transition to whatever a situation necessitated. Imogene could be browbeaten housewife or femme fatale at a moment’s notice. On one hand, her desires were base and gaudy, but she also masterminded a complex scheme to funnel much of her husband’s wealth to herself and family members.
Unlike other accounts of George and Imogene, my research revealed how devious she had been from the start of her relationship with her husband. Much of Imogene’s early life had never been uncovered, particularly the lengths she went to attract a modicum of fame.
Yet, at the same time, Imogene played a dangerous game, dancing on the edge of a cliff. She may have thought she understood George, but in the end, she had no clue to the depths of violence and anger Remus could unleash.
Imogene grew up in Milwaukee dreaming of a life bigger and more glamorous than her working class roots. What I found in researching her life is that she was constantly playing with her identity by using different names, from “Gussie” and “Gene” to “Susan” and others.
Trying these names and different identities on like masks, Imogene hoped to become wildly famous and rich, living out an aristocratic life that she saw around her. I also uncovered a number of crazy attempts Imogene made to get her name in the newspapers, which was one of the best ways to increase notoriety in the early twentieth century. She would send “news” to reporters, and for someone with no formal training, had several pieces picked up.
For example, around the time the story broke about her breaking up George’s first marriage, using the name “Gene Holmes,” she had a list of tips for a wife to follow to keep her husband from “becoming a wild man.” Reporters who ran the story did not miss the irony of the highly-publicized “love triangle” that had been in the papers for months.
Even more overtly, Imogene told a friend shortly after Remus moved in with her that she planned to “roll him for his roll” and that she “would marry him if I have to” to get his money. George was already famous, flashy, and probably looked like a great catch for Imogene. She won him over and eventually got all the riches in the world. However, she couldn’t have had any idea at that time what a depraved person he would become.
The Bourbon King, The Inside Story: Government Corruption, Then and Now
A popular political cartoon representing how the nation has been crushed under the weight of the Teapot Dome scandals.
Widely considered the “best dressed man in Washington,” Jess Smith served as Attorney General Harry M. Daugherty’s confidante, friend, nurse, and bagman for the mountains of cash he was able to extort from America’s bootleg barons. When he committed suicide on May 30, 1923, it ended what little hope Remus had from staying out of jail.
The Bourbon King offers a window into government corruption at the highest levels. Any lessons we can learn for understanding today’s political scene?
Presidential corruption is a delicate matter. Incredibly partisan, one side sees something that the other does not. History helps sort out details and brings new evidence to light, but then how do we deal with scandal as it takes place?
George Remus built a far-reaching bribery network that stretched from the suburban Cincinnati police to the Harding White House. He virtually taught Newport, Kentucky, about graft, which enabled the city to become a model for corruption and vice. Decades later, the mafia would move into Newport and see the city as a model for Las Vegas.
Much of the corruption Remus took advantage of came directly from the Prohibition Bureau, particularly as enforcement began. At every level, “Prohis" (the nickname given to agents tasked with enforcing Prohibition) fell to corruption and payoffs.
For example, many leaders at the state level issued whiskey certificates—paper documents that gave the holder the ability to sell liquor legally to pharmacies, hospitals, doctors, and others for “medicinal usage”—for a hefty fee.
“They received considerations,” Remus explained. “Otherwise those withdrawals would never have come to the respective distilleries that I was owner of.”
As a result of the permutations, trust evaporated and criminality ruled, particularly as officials in the Harding administration learned that they could be so dishonest.
Much of the underhanded maneuvers originated in Attorney General Harry M. Daugherty’s office and ran through Jess Smith, his bon vivant friend and confidante. Jess ran interference for Daugherty and his Ohio cronies linked to Harding’s White House. The money changed hands, which fit with Remus’s worldview of how men acted when they had a deal, but he had no guarantee that Smith could do what he said.
Amidst this setting, and with his own loose lips, could Remus possibly keep his central bribe secret? A journalist reported that he heard a rumor around town about George, explaining, “He was once heard to boast that he was immune from prosecution because he had the ear of the private secretary of a cabinet officer.”
The bribery network soon crumbled…
On May 30, 1923, Jess startled awake in the middle of the night. He drew a pistol from a bedside drawer, stumbled to the bathroom, and lay down on the floor. Positing his head on the side of a wastebasket, Jess put the revolver to his temple and pulled the trigger.
Smith killed himself a little more than two months before the shocking death of Warren G. Harding, who declined quickly on a trip out West and ultimately passed away on August 2, 1923, only 57 years old.
The Ohioan was wildly popular at the time and mourners lined the train route that brought the dead president back to the nation’s capital. Only after his death would the full weight of his scandal-ridden administration become unraveled by a series of congressional investigatory committees and reporters hot on the trail of his Cabinet members and their cronies, many who seemed to specialize in corruption. For George, the deaths of Smith and Harding left him with little hope. Worse, the tragedies severed his ties to Daugherty.
“Misfortune came fast, suddenly,” Remus said. “Jess Smith was found dead in his bathroom. President Harding died. The Senate called for the impeachment of Harry Daugherty. The game was over. I had no place to turn.”
Shortly after President Harding died in office, many scandals came to light that revealed the full extent of his administration’s corruption. However, Harding was given a kind of free pass.
Today, with President Donald Trump, the accusations regarding corruption are much more vocal and public. Events that transpired in Harding’s era demonstrated how bad actors could really line their own pockets by using their power in various schemes.
Modern presidents are not given the same benefit of the doubt. The amplification of outrage based on social media and a more pervasive news cycle means that cries of government corruption are going to be louder and shriller.
The challenge for us today is attempting to determine how much of the dishonesty is real and what might be condensed down to partisanship. Calvin Coolidge — Harding’s successor — watched a series of Congressional investigations into corruption by Harding Cabinet members. He constantly worried about how those spectacles would influence voters’ minds in the 1928 election.
As long as the economy boomed, observers gave Harding and Coolidge a free pass. At the time, the scandals did not topple their administrations.
Today, however, the notion of a free pass is laughable as a president’s every move is scrutinized by a highly-partisan citizenship.
The media—crippled by the financial crisis that has left the industry in shambles over the last two decades—responds by chasing every sensational detail, forced to feed the bile back to consumers, hoping that their anger will result in advertising dollars and measured in online “impressions.”
The corruption of the Harding administration—with George Remus at its center—provides a case study in corruption by White House subordinates who realized how swiftly they could fleece the system. Today, are we too distracted by the daily shouting to scrutinize the details as they unfold just below the surface?
The Bourbon King, The Inside Story: Prohibition and Marijuana
Can we learn from Prohibition in thinking about issues regarding the legalization of marijuana?
My favorite history books provide deep insight the issues of the past and act as a kind of guide for addressing contemporary concerns. I had this idea in mind when writing The Bourbon King — how do we think about marijuana and other lifestyle choices regulated and legislated by the government?
We are still learning the lessons of Prohibition a century later. The most destructive aspect of the dry era was that it took a significant human toll on America.
Many lives were wasted, from people poisoned by tainted alcohol to those killed in enforcing the Volstead Act or attempting to circumvent the law. We have seen similar scenarios play out over the last several decades with marijuana legislation and enforcement.
During Prohibition and with weed over the last several decades, a significant air of lawlessness became commonplace. The nation still deals with these issues now. For instance, people travel between states that have legalized recreational and medical marijuana and those that still criminalize it.
Texas Senator Morris Sheppard, the “father of Prohibition”
We are still learning the lessons of Prohibition a century later…Many lives were wasted…a major human toll on America…We have seen similar scenarios play out over the last several decades with marijuana legislation and enforcement.
The Bourbon King, The Inside Story: George Remus and Al Capone
How does George Remus compare to Al Capone?
Without George Remus, there is no Al Capone.
Every city in America had underworld operatives long before Prohibition. Bootlegging existed, whether it was running the product of home stills to avoid government taxes or bringing cheap liquor into the United States from Mexico.
When the dry laws kicked in, rumrunning became big business. In America’s largest cities, like Chicago, bosses like Johnny Torrio quickly realized that America’s thirst needed quenched and by smuggling liquor, they could make untold millions.
Rather quickly, criminal kingpins realized that they needed booze to thrive. Remus provided that liquor and enabled men like Torrio, and his successor Al Capone to create empires. Other liquor masterminds existed, so Remus was not alone in getting booze to mob bosses, but his network was extensive and centered on selling the highest quality Kentucky bourbon.
Selling “the good stuff” led to connections between Torrio’s Windy City operation and Remus’s headquarters at Death Valley. George Conners, Remus’s top lieutenant, spoke at length about his salesman trips to Chicago to funnel bourbon into the large market there. Torrio also had ties to the Cincinnati metro area, marrying a woman from Northern Kentucky and having family in the area.
While George and Al had similar interests in selling booze and making as much money as possible, on a personal level, Remus was a generation older than Capone and some of the other “name” mafia bosses, like Lucky Luciano and Meyer Lansky, the friends who operated at the feet of criminal mastermind Arnold “the Big Brain” Rothstein in New York City. After Rothstein’s murder, Luciano and Lansky became kingpins themselves. Men like these were career criminals. When bootlegging turned vicious, they were more willing to kill or incite violence and murder to achieve their end goals.
Remus, although no stranger to gunfights or ordering his men to protect his product with gun play, was a product of the Gilded Age. George’s first instinct was to respond to a threat with his fists or the gold-tipped, weighted cane that he carried as both a style statement and weapon. As Prohibition went on, it became a shoot-first world.
People often ask why Remus didn’t get back into bootlegging in June 1928 after his stints behind bars and at the Lima State Hospital for the Criminally Insane. There are many potential answers, but most directly: without money or henchmen, Remus could not reestablish his bourbon empire after winning his freedom. George would have needed an army to reclaim even a portion of his empire, but after Imogene and Franklin Dodge decimated his fortune, he could not afford to rebuild.
This is only a small tidbit of the complexity of Remus’s interactions with his mafioso colleagues. The full story will make more sense after reading The Bourbon King.
The famous Rathskeller bar in the Seelbach Hilton Hotel in downtown Louisville. Allegedly, Remus and Capone drank together at the Rookwood Pottery tile-encrusted grotto, one of the most stunning displays of Rookwood from the early twentieth century.
The Bourbon King, The Inside Story: George Remus as a Business Leader
At the height of his power, George Remus purchased an office complex at 225 Race Street on the southwest corner of Race and Pearl Streets, renaming it the “Remus Building.” The lobby tile display (allegedly from the famous Rookwood Pottery) spelled out “Remus,” which he thought demonstrated his authority. For his second-floor office space, Remus spent $75,000 on lavish furniture, accessories, and equipment, as well as a personal chef.
(Courtesy Public Library of Cincinnati and Hamilton County, Cincinnati History Slide Collection)
George Remus as a Business Leader
Remus cashed out in Chicago and took his fat stacks to Cincinnati, the epicenter of the bourbon and beer industries in the early twentieth century. He parlayed his life earnings into a fortune that some estimate reached $200 million, which would be many billions of dollars today over the course of about two and a half years.
Remus realized that he could control every aspect of the bootlegging business, from production to distribution via other rumrunners and liquor operatives, while also selling directly to consumers. He called this idea “the circle,” which was probably modeled on what J. D. Rockefeller had done in the oil business. “Cornering the market” was a popular idea in the 1920s, a decade and a half after President Theodore Roosevelt had criticized business leaders for attempting to create corporate monopolies.
“Remus was to bootlegging what Rockefeller was to oil.”
— Paul Y. Anderson, St. Louis Dispatch
Basically, like Rockefeller in oil or J. P. Morgan in steel, George wanted to create a network that controlled all aspects of the bourbon industry, from creating the product in Kentucky distilleries to shipping and distribution, and then through the sales process. If he controlled all these points—thus creating the circle—he would dominate the market.
Creating this national network took a lot of money and a lot of hubris. Remus had both in spades. He pulled it off, but in the end, faced some of the same challenges businesses have always faced: lack of talent to manage the organization and deals that fell through. Remus needed henchmen that were as smart as him and he had trouble finding them. Then, his “sugaring” network—the term for bribery in the 1920s—fell through. These challenges essentially put him out of business.
Check out The Bourbon King: The Life and Crimes of George Remus, Prohibition’s Evil Genius for the whole story, including how Remus assessed his own abilities as a corporate leader.
The Bourbon King, The Inside Story: George Remus as a High-Flying Defense Attorney
George Remus became a top criminal defense attorney in Chicago. What made him so successful in the courtroom?
George Remus transitioned to attorney at a time when the Chicago economy boomed and new residents poured into the region. His early work centered on labor law, representing several large Windy City unions. The efforts put George in the circle of famed attorney and human rights activist Clarence Darrow.
Both men abhorred the death penalty and Remus gravitated to criminal defense work, just as Darrow had done earlier in his career. What set George apart was his willingness to do anything to win, particularly if he could get a death row sentence reduced to jail time.
When Remus put his considerable intellectual and physical efforts toward a legal career, he ruffled the existing “old boy’s network,” which saw him and his second-rate legal training as an imposition on the establishment they had crafted (he most likely faced a great degree of anti-German discrimination as well). George charged ahead, though, engaging in local Republican politics and serving as a leader in a new legal society aimed to upend the status quo.
No one could deny Remus’s dedication, but his tactics upset many of his colleagues.
George Remus photographed during his time as an attorney in Chicago
If a legal eagle were Remus’s friend, he might refer to George as the “Napoleon of the Bar” as a way of acknowledging his legal acumen. Others, however, called George “weeping pleading Remus,” because his theatrics were viewed as outside the bounds of decorum.
George’s escapades were legendary—from starting fistfights with opposing counsel to drinking down poison in front of the jury to proved his client not guilty (luckily, George had mixed up the antidote and taken it beforehand). Many of Remus’s trials were covered by reporters regionally and nationally. Chicago Tribune journalists knew they could call on George for a hot soundbite.
Although Remus might wildly gesticulate and fly into near rages to defend a client, jurors also remarked about how mesmerizing Remus was in the courtroom. George seemed to have a sixth sense regarding when a well-time antic might persuade a jury or distract them from the prosecution’s case. He possessed a natural charisma and magnetism that defined his legal career.
The Bourbon King, The Inside Story: George Remus's Early Pharmacy Career
Remus during his pharmacy years, pictured standing in front of the nine-story Geo. Remus and J.A. Taggart Office Building at 4520 North Clarendon Avenue in Chicago, near Lake Shore Drive and on the edge of Buena Park and Uptown. Lillian is in the driver’s seat, while Romola is sitting behind her.
George Remus began his career as a pharmacist. In what ways did that job impact his later life?
George Remus’s life as a pharmacist demonstrated his wide-ranging intellect and dedication. He learned the trade “on the job,” but also took coursework to solidify his understanding of the science of that era.
In the late nineteenth and early twentieth centuries, pharmacists were more like doctors (particularly in areas like suburban Chicago where there were extensive immigrant populations). Remus interacted with his customers, dispensing medical advice and treating minor ailments. He even got an optometry certification so he could be called “Dr. Remus.”
The drugstore also served as a center of the local community, so Remus became a well-known figure…and he loved the adulation that came with the title and sense of responsibility. The years in the pharmacy business were crucial in his development and self-identification.
However, the career also turned him off to medicine. He thought much of what stood in for “science” was actually quackery. Yet, at the same time, he embraced his ability to fleece the public by introducing a line of “Remus” brand pills, like others in the era (think “Lydia E. Pinkham’s Vegetable Compound”) that were all the rage. He sold these treatments to large drug wholesalers across the Midwest.
The money Remus made in this line of business and then opening his own drug companies enabled him to see how easily he could make money based on his smarts.
As a pharmacist, Remus also learned a great deal about the law and legal system, which would serve him well later as an attorney and bootlegger. He put this study of drug regulations and setting up pharmacies to work as a bootlegger, always searching for legal loopholes to the Volstead Act, once Prohibition became law.
The Bourbon King, The Inside Story: Why Write about George Remus
How did you discover the story of George Remus, and why did you decide to write a book about him?
Imagine having a topic in your head for 17 years!
I stumbled across George Remus about 17 years ago when Stanley Cutler, an esteemed American historian and scholar, asked me to write about bootlegging for the Dictionary of American History.
Remus’s story was so epic that I couldn’t get it out of my mind. The “Bootlegging” entry had to be concise, so I didn’t get much of an opportunity to expand on the Remus story, but I snuck him in, as well as mentions of Cleveland and Pittsburgh.
Here’s that bit from the essay:
Given the pervasive lawlessness during Prohibition, bootlegging was omnipresent. The operations varied in size, from an intricate network of bootlegging middlemen and local suppliers, right up to America's bootlegging king, George Remus, who operated from Cincinnati, lived a lavish lifestyle, and amassed a $5 million fortune. To escape prosecution, men like Remus used bribery, heavily armed guards, and medicinal licenses to circumvent the law. More ruthless gangsters, such as Capone, did not stop at crime, intimidation, and murder.
— “Bootlegging” Dictionary of American History, 2003
Although researched and written so long ago, I still see bits of my personal writing style that persists. “Pervasive lawlessness” is a stylistic point, as well as the pacing of the sentence.
Later, in 2013, I published a biography of The Great Gatsby, which I had been researching and writing for years. Obviously, the work on the book forced me to continue thinking about this crazy bootleg king, particularly since so many people began writing that he was the inspiration for Jay Gatsby, rather than just one of several.
[Spoiler alert: the link between Jay Gatsby, F. Scott Fitzgerald, and George Remus is an important discussion in The Bourbon King and the beginning of one of America’s great literary mysteries that readers will really enjoy.]
The more I thought about the bootleg king, the more it seemed that no one had really fully captured Remus or put him within the context of American history. His epic tale illuminates and interrogates the early twentieth century, Prohibition, Constitutionality, and many other topics that continue to confound people today.
George Remus also fit neatly into my cultural historian and biographer wheelhouse: big topic, historically significant, and interesting links from that era to what we are experiencing today. I found that there were still many undiscovered aspects to Remus’s story and there were untapped archives, so I barreled ahead.
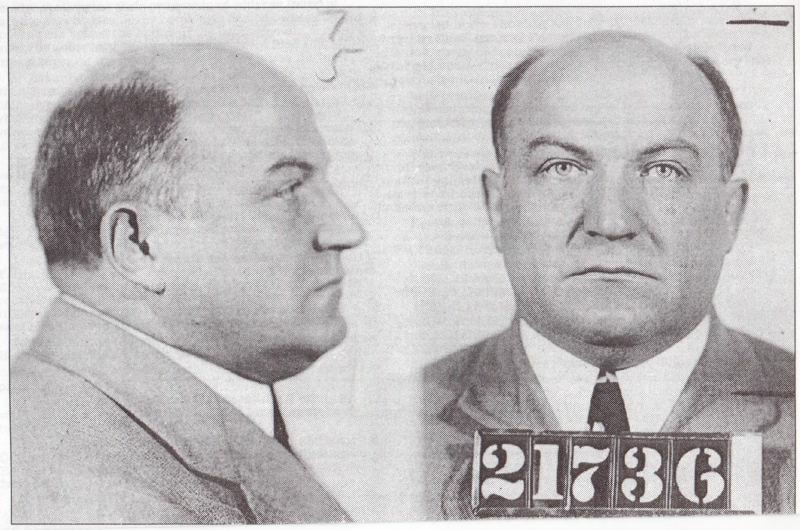
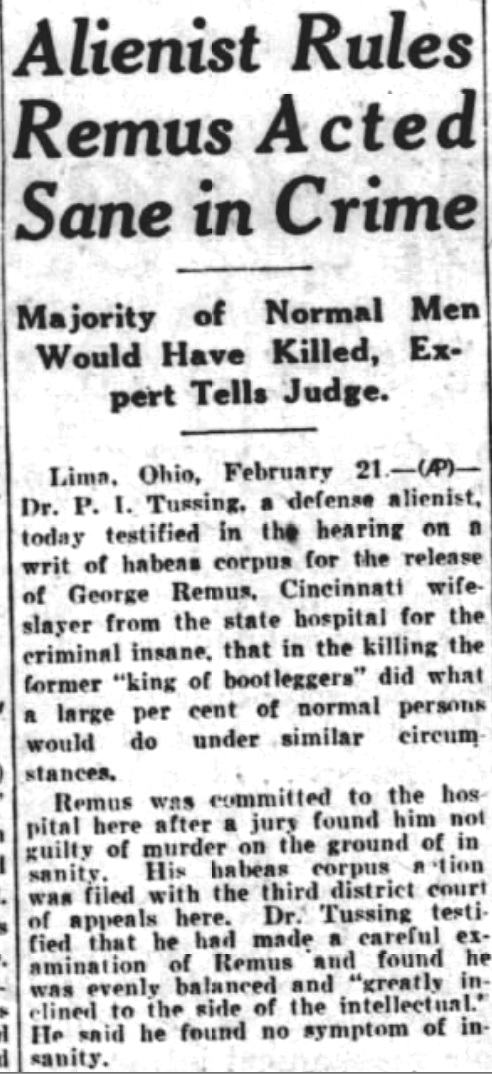
George Remus, King of the Bootleggers: Insanity and Murder
George Remus, the former King of the Bootleggers, fought to prove that he was sane in February 1928, two months after a jury declared the murder of his wife Imogene “transitory maniacal insanity” and that he should go free.
Read more